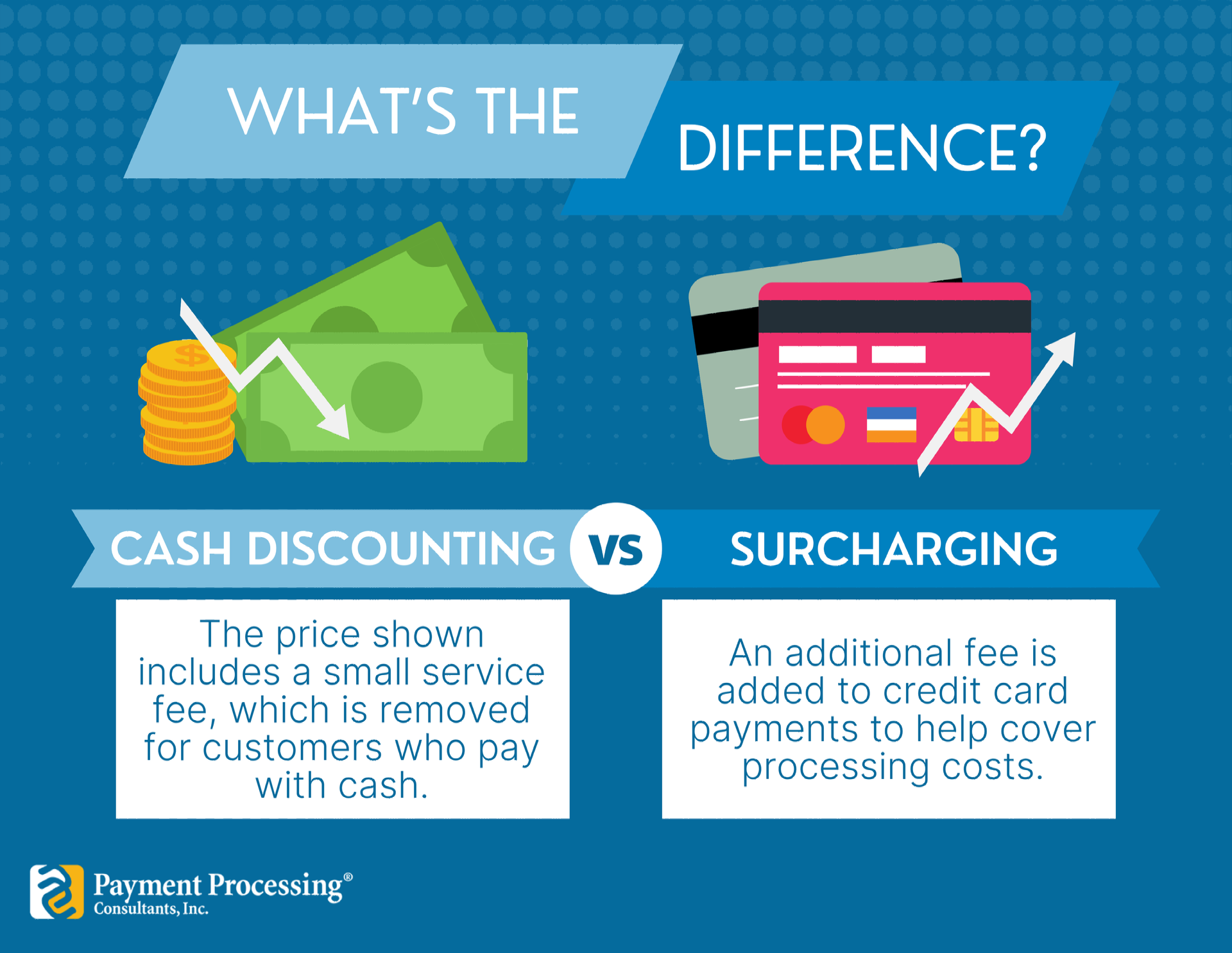
By Samantha Dinardo
•
November 7, 2024
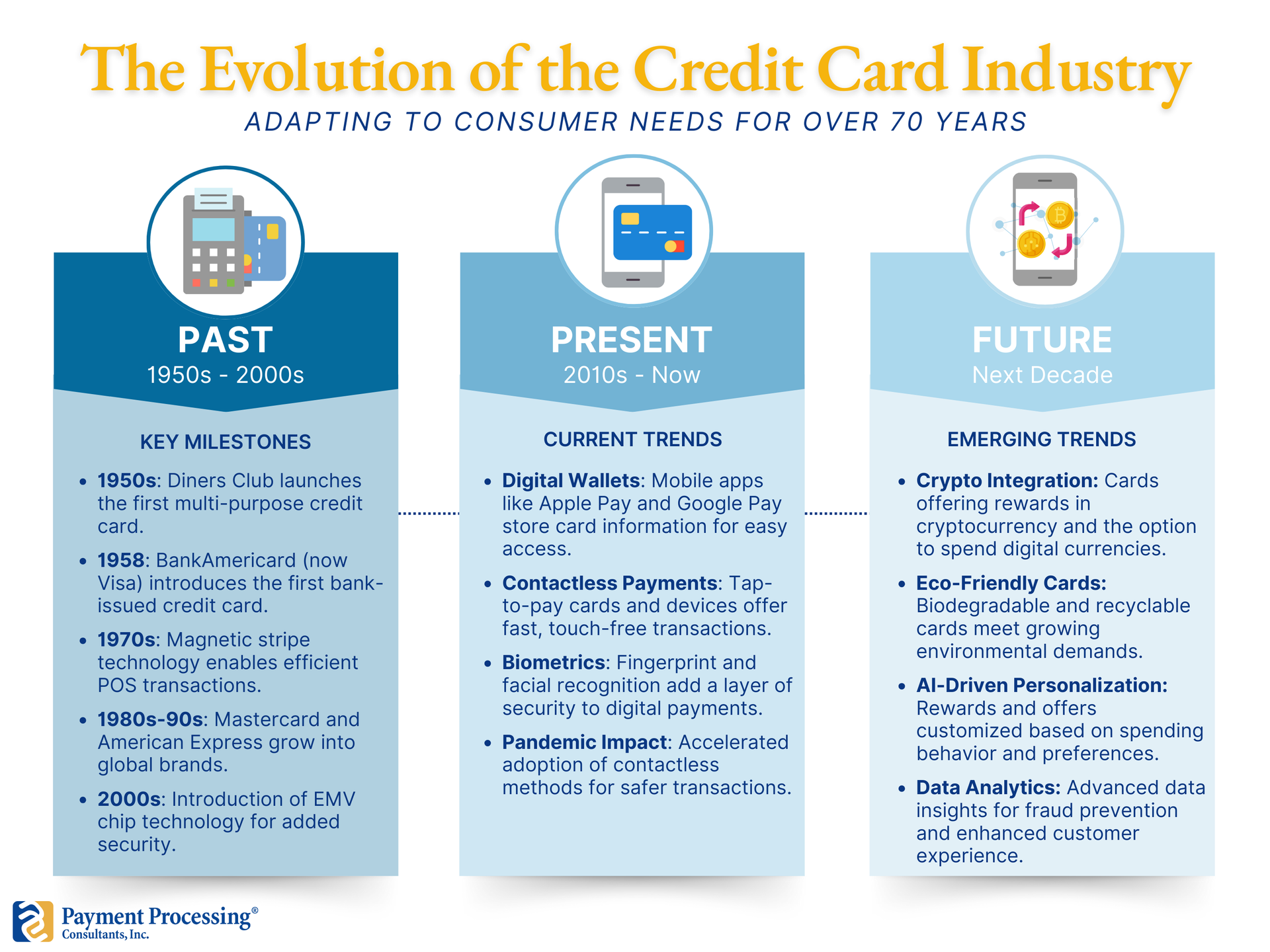
The credit card industry has come a long way since its inception, evolving from a simple concept of deferred payments to a sophisticated system embedded with digital features, global reach, and advanced fraud protection. With rapid technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and regulatory challenges, the future of the credit card industry presents both exciting opportunities and critical challenges. This article will explore the evolution of the credit card industry, key trends shaping its future, and the challenges that industry players will face in the coming years. The Evolution of the Credit Card Industry 1. Early Beginnings The credit card industry traces its roots back to the early 20th century, when various retail stores began offering credit to trusted customers. In 1950, the Diners Club introduced the first multi-purpose charge card, which allowed holders to pay at a variety of restaurants and stores, laying the groundwork for modern credit cards. The innovation caught on, leading to the launch of the first bank-issued credit card, BankAmericard, in 1958. This card would eventually evolve into Visa, one of the world’s leading payment networks. The credit card revolution expanded globally, and by the 1980s, major players such as Mastercard and American Express became household names. 2. The Digital Shift The digital revolution of the late 20th century transformed credit cards into tools that could be used virtually anywhere in the world. The development of electronic payment networks enabled the shift from paper-based to electronic transactions. This era saw the launch of magnetic stripe technology, enabling more efficient and secure transactions at point-of-sale (POS) terminals. By the 2000s, chip technology (EMV) was introduced, further enhancing security and reducing fraud. 3. The Rise of Mobile and Contactless Payments In the last decade, credit cards have adapted to the rise of digital wallets and contactless payment methods. Consumers can now store credit card information on mobile devices through apps like Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay, making transactions quick and seamless. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of contactless payments, with people seeking safer, touch-free options. This shift has given rise to new payment technologies, including biometrics and QR codes, which are further redefining the credit card experience. Trends Shaping the Future of the Credit Card Industry As the industry continues to evolve, several key trends are shaping its future: 1. Digital-First Credit Cards and Virtual Accounts Digital-first credit cards are designed for online and mobile-first usage, often with physical cards as an optional feature. These cards appeal to tech-savvy consumers who prioritize convenience and security. Virtual accounts, which generate temporary credit card numbers for one-time use, are also becoming popular for online transactions. With digital-first options, consumers benefit from instant access, flexible payment options, and an added layer of security against fraud. 2. Embedded Finance and Open Banking Embedded finance integrates financial services directly into non-financial platforms, enabling consumers to access credit card features directly within apps they frequently use, such as e-commerce or social media. Open banking, which allows third-party financial service providers to access consumer banking data (with permission), enhances this by providing more personalized credit options. Together, embedded finance and open banking are enabling a frictionless customer experience, where credit is more accessible and tailored to individual needs. 3. Personalized Rewards and Loyalty Programs The future of loyalty programs is personalization. With the help of AI and data analytics, credit card issuers can now create rewards programs tailored to individual spending patterns. This shift from generalized points to more meaningful, customer-specific rewards is helping brands build stronger customer loyalty. For instance, a frequent traveler might receive enhanced rewards for flights and hotels, while someone who shops at local retailers might receive exclusive discounts and cashback options at those stores. 4. Advanced Fraud Detection and Prevention Fraud detection and prevention are becoming increasingly sophisticated with advancements in machine learning and artificial intelligence. Modern fraud systems analyze vast amounts of transaction data in real time, identifying unusual patterns and flagging suspicious activity. This proactive approach helps protect cardholders from unauthorized charges and boosts overall confidence in credit card use. As fraud techniques continue to evolve, so too will the technology used to combat it. 5. Environmental and Social Responsibility Initiatives Consumers are increasingly prioritizing brands that align with their values, and the credit card industry is responding. More issuers are launching eco-friendly cards, supporting reforestation, and investing in carbon offset programs. Some credit cards now feature rewards linked to sustainable purchasing or donations to social causes. By adopting environmentally and socially conscious practices, the industry is enhancing its appeal to the growing demographic of ethically-minded consumers. 6. Cryptocurrency Integration With the rise of digital currencies, credit card issuers are beginning to incorporate cryptocurrency features. Some credit cards offer rewards in Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies, while others allow cardholders to spend crypto at traditional merchants. As digital currencies gain popularity, credit card companies are likely to introduce more crypto-compatible features, creating a bridge between traditional finance and the digital asset economy. Challenges Facing the Credit Card Industry Despite these trends, the industry faces several challenges that could impact its growth: 1. Regulatory Scrutiny and Compliance With increased data access and the integration of third-party services, regulators are tightening standards around data privacy and security. Compliance with regulations like the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) requires ongoing investment in data security. Additionally, regulatory agencies are implementing stricter standards around credit risk, cross-border transactions, and fraud detection, posing challenges for issuers seeking to innovate quickly while staying compliant. 2. Competition from Fintech and Alternative Payment Methods The credit card industry is facing fierce competition from fintech solutions that offer direct, consumer-friendly payment options like buy now, pay later (BNPL) services and digital wallets. These alternatives provide flexible payment terms and often lower fees, attracting consumers who are wary of interest charges and fees associated with traditional credit cards. Credit card companies will need to innovate and offer comparable flexibility and value to remain competitive. 3. Rising Cybersecurity Threats As cybercriminals become more sophisticated, protecting sensitive credit card data is a growing challenge. Data breaches can have devastating impacts on both customers and credit card issuers, leading to financial losses, reputational damage, and regulatory penalties. The industry must continuously invest in state-of-the-art cybersecurity measures and customer education to mitigate the risk of data breaches and fraud. 4. Adapting to Changing Consumer Preferences Consumer expectations around convenience, transparency, and ethical responsibility are reshaping how people view credit cards. Younger generations, in particular, are wary of traditional credit models that come with high fees and interest rates. Instead, they are drawn to options that offer flexibility, transparency, and align with their values. The credit card industry must adapt by offering more customer-centric options, such as interest-free installment plans, fee transparency, and eco-friendly practices. 5. Economic Uncertainty and Credit Risk Economic downturns can impact credit card issuers’ revenue, as consumers reduce spending and become more cautious with credit. Furthermore, during recessions, delinquency rates on credit card balances often rise, increasing credit risk for issuers. The credit card industry must therefore balance growth initiatives with sound risk management strategies to safeguard against economic fluctuations. The Future of the Credit Card Industry The credit card industry’s future is likely to be defined by a blend of technological innovation, regulatory adaptation, and customer-centric strategies. To thrive, industry players must embrace flexibility, prioritize customer preferences, and ensure security. Here are a few predictions: Real-Time Data and AI-Powered Personalization: Credit card companies will increasingly leverage real-time data analytics to provide ultra-personalized offerings that reflect each customer’s lifestyle and spending habits. Expansion of Credit Ecosystems: The integration of credit services within broader ecosystems, such as digital wallets and e-commerce platforms, will offer customers more seamless access to credit, anytime and anywhere. Focus on Sustainability: As environmental concerns continue to grow, credit card companies may further develop eco-conscious products, such as biodegradable cards or rewards that incentivize sustainable spending. Collaboration with Fintechs: Rather than compete, credit card issuers may increasingly partner with fintech companies to leverage each other’s strengths, such as embedding credit services within BNPL apps or offering cryptocurrency options. As the industry evolves, credit card providers that proactively adapt to these trends, address challenges, and prioritize customer needs will continue to succeed in an ever-competitive landscape. The next decade promises a transformative journey for the credit card industry as it becomes more digital, data-driven, and responsive to the needs of a new generation of consumers.